1 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所强激光材料重点实验室,上海 201800
2 中国科学院大学,北京 100049
钕玻璃激光放大片在热恢复后的剩余温度场对于光束退偏和波前畸变具有重要的影响。当冷却过程中出现不对称情形,将导致剩余温度场的不对称,从而影响到高功率激光光束发次之间的重复性。本文在对N41型钕玻璃四周包边侧弱冷和强冷所导致的剩余温度场分布特征进行模拟分析的基础上,重点研究了包边侧不对称冷却所导致的剩余温度场的变化。这种变化的程度与钕玻璃四周包边侧冷却的强弱有关,并进一步分析了由弱冷转为强冷时钕玻璃激光放大片的通光面和四周包边界面上各自的散热量。
材料 钕玻璃主放大片 有限元模拟 剩余温度场 不对称冷却 光束稳定性 激光与光电子学进展
2023, 60(21): 2116001
1 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所, 强激光材料重点实验室, 上海 201800
2 中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
3 中国核电工程有限公司, 北京 100840
钼是动力堆乏燃料后处理产生的高放废液中主要的核素之一。MoO3在铁磷酸盐玻璃中的溶解情况以及MoO3含量变化对玻璃结构的影响是动力堆高放废液固化用铁磷酸盐玻璃配方研究的重点。在成分为60%P2O5-19%Fe2O3-8%Al2O3- 13%Na2O (摩尔分数)的基础玻璃中, 加入1%~8% (摩尔分数) MoO3, 采用熔淬法制备一系列样品。X射线衍射、电子探针显微分析用于物相和显微形貌分析, Raman光谱、X射线光电子能谱和Mssbauer谱用于结构分析。MoO3实际含量小于等于6.38%时, Mo可以完全溶入到玻璃结构中, 不形成析晶和分相。MoO3含量大于等于4%时, Mo离子以[MoO6]结构存在并形成Mo-O-P键。Q1和Q2单元是玻璃相中的主要结构, 且Q1单元的相对含量随着MoO3含量增加。随着MoO3含量增加, Fe3+相对含量略有减少, 而Mo离子价态不变。
钼 铁磷酸盐玻璃 玻璃结构 价态 molybdenum iron phosphate glass glass structure valence state

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Materials for High Power Laser, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai201800, China
2 Center of Materials Science and Optoelectronics Engineering, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing100049, China
This paper investigates the monolithic edge-cladding process for the elliptical disk of N31-type Nd-doped phosphate laser glass, which will be utilized under liquid cooling conditions for high-power laser systems. The thermal stress, interface bubbles and residual reflectivity, which are due to high-temperature casting and bonding during the monolithic edge-cladding process, are simulated and determined. The applied mould is optimized to a rectangular cavity mould, and the casting temperature is optimized to 1000°C. The resulting lower bubble density makes the mean residual reflectivity as low as 6.75 × 10-5, which is enough to suppress the amplified spontaneous emission generated in the Nd-glass disk, and the resulting maximum optical retardation is converged to 10.2–13.3 nm/cm, which is a favourable base for fine annealing to achieve the stress specification of less than or equal to 5 nm/cm. After fine annealing at the optimized 520°C, the maximum optical retardation is as low as 4.8 nm/cm, and the minimum transmitted wavefront peak-to-valley value is 0.222 wavelength (632.8 nm). An N31 elliptical disk with the size of 194 mm × 102 mm × 40 mm can be successfully cladded by the optimized monolithic edge-cladding process, whose edge-cladded disk with the size of 200 mm × 108 mm × 40 mm can achieve laser gain one-third higher than that of an N21-type disk of the same size.
interface bubble monolithic edge-cladding process N31-type Nd-doped phosphate laser glass residual reflectivity stress birefringence High Power Laser Science and Engineering
2022, 10(2): 02000e14
1 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所强激光材料重点实验室,上海 201800
2 中国科学院大学,北京 100049
3 中国核电工程有限公司,北京 100840
Joule加热陶瓷炉玻璃固化技术因其熔炉尺寸不受限制、单位时间内玻璃产率高、贵金属相容性好等优势,在高放废液玻璃固化领域占据主要地位。介绍了美、俄、德、日等国的Joule加热陶瓷炉工程应用情况和Joule加热陶瓷炉的各项关键单元技术研究进展。未来Joule陶瓷炉玻璃固化技术的发展重点为在研发关键材料(耐火材料、合金材料)的基础上,根据高放废液成分,设计高熔池温度、高玻璃产率、贵金属相容性好的Joule加热陶瓷炉,以提高高放废液玻璃固化的减容比和经济性。
Joule加热陶瓷炉 玻璃固化 放射性废物 固化体 Joule heated ceramic melter vitrification radioactive waste waste form
1 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所强激光材料重点实验室, 上海 201800
2 中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
硬包边是激光钕玻璃减少放大自发辐射和抑制寄生振荡的包边技术之一,残余应力是硬包边的一个重要参数。详细描述了激光钕玻璃硬包边过程中残余应力的来源,并利用有限元分析软件COMSOL Multiphysics,对硬包边浇注熔接过程中不同膨胀系数匹配条件和不同包边玻璃浇注温度下的残余应力分布进行了数值模拟。结果显示,激光钕玻璃和包边玻璃的膨胀系数差异愈小,产生的残余应力愈小;包边玻璃浇注温度愈高,则产生的残余应力愈大。硬包边实验结果表明:包边玻璃的膨胀系数和激光钕玻璃的膨胀系数愈相近,则残余应力就愈小,当包边温度在700~1200 ℃范围内时,残余应力随着包边温度的增加而增大。模拟结果与实验结果吻合,所以在硬包边的浇注熔接过程中,为了使残余应力最小,最佳策略是激光钕玻璃的膨胀系数和包边玻璃的膨胀系数尽量接近甚至相等,且包边温度尽量低。
材料 激光钕玻璃 硬包边 有限元分析 激光元件 应力双折射率 残余应力
红外与激光工程
2020, 49(12): 20201081
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
A novel four light ray path test method for measuring residual reflectance has been presented. Residual reflectance spatial distribution at a cladding interface was measured using the technique. Residual reflectance could be on the order of 10?5 by matching the refractive index of Nd:glass, polymer, and cladding glass and eliminating defects in the adhesive layer. Residual reflection spatial distribution appears to be similar to Newton rings due to the edge surface flatness. The relationship between the residual reflectance and the edge surface flatness was discussed, and the results revealed that the edge surface flatness is very important during the cladding process.
residual reflectance edge cladding Nd:glass amplifier Chinese Optics Letters
2020, 18(9): 091402
中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所激光玻璃研发中心, 上海 201800
报道了磷酸盐激光钕玻璃的连续熔炼线,以及采用连续熔炼工艺获得的400 mm 口径N31 钕玻璃的主要性能。连熔所制备的N31-35 钕玻璃的掺杂离子浓度为3.47(±0.02)×1020 cm-3;1053 nm 处的折射率为1.5336±0.0005;400 nm 处的吸收系数平均值为0.098 cm-1;1053 nm 处的激光波长损耗为0.13~0.15% cm-1;3000 cm-1 处的吸收系数平均值为0.83 cm-1。400 mm 口径连熔N31 钕玻璃的透射波前畸变在633 nm 处小于λ/3 波长。采用1053 nm、脉冲为3 ns激光作用下连熔钕玻璃的体破坏阈值大于40 J/cm2。结果表明,在N31 钕玻璃的连续熔炼工艺中,除铂金和除水都取得了很好的效果。
光学制造 激光钕玻璃 连续熔炼工艺 损耗 增益系数
1 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所, 上海 201800
2 中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
为减少放大自发辐射和抑制寄生震荡,需在激光钕玻璃片侧面粘接一层吸收介质包边玻璃,其中,包边残余应力是粘接的一个重要参数。详细描述了激光钕玻璃与包边玻璃在包边粘接过程中粘接界面附近残余应力的来源,实验讨论分析了精密退火、加工、包边粘接等对界面附近残余应力的影响。结果表明,退火过程中的边缘应力对粘接界面附近残余应力影响比较大,且包边面加工面型匹配越差,则界面附近残余应力越大,而低收缩率和低模量的粘接胶对界面附近的残余应力影响较小。
激光技术 激光钕玻璃 包边 残余应力 应力双折射
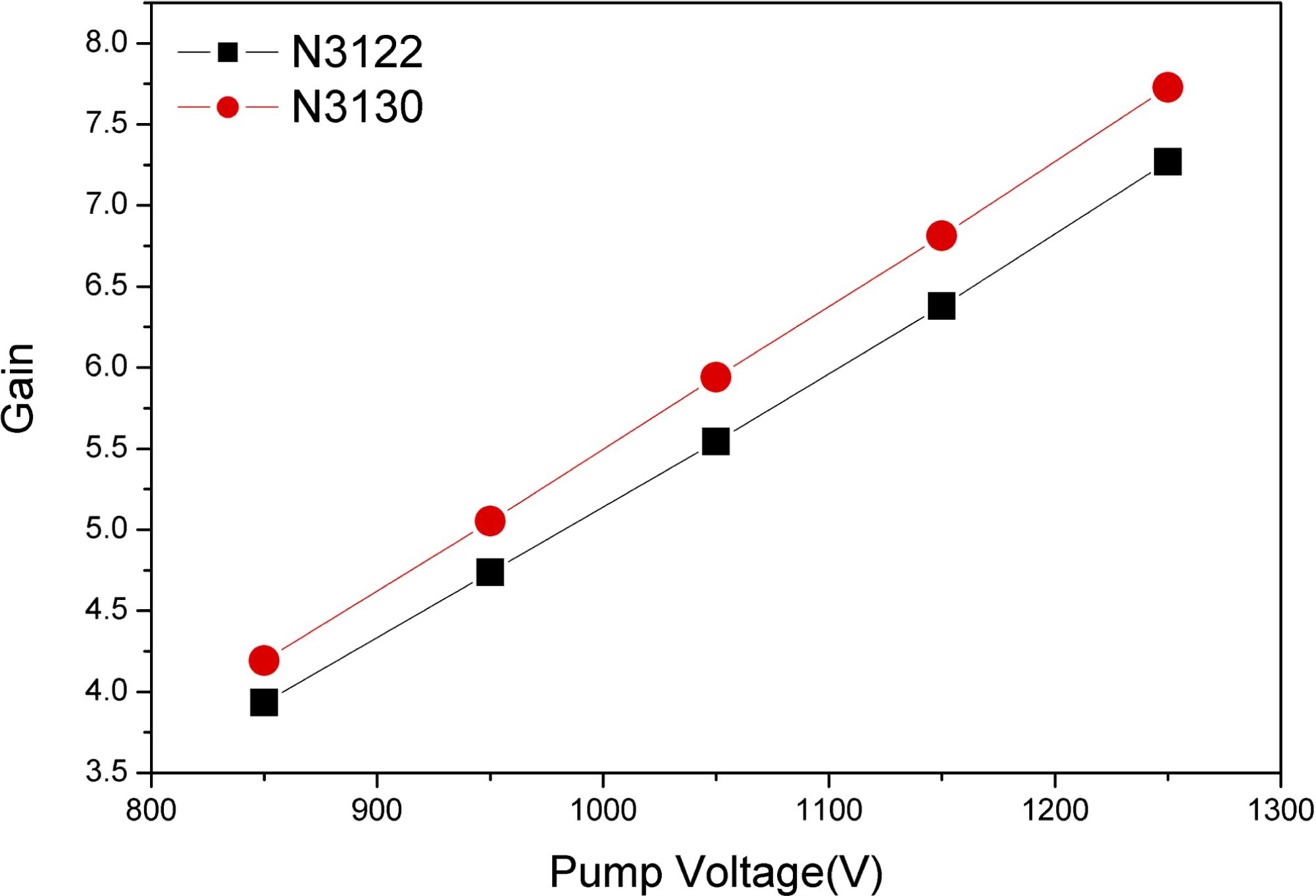
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
Large aperture Nd:phosphate laser glass is a key optical element for an inertial confinement fusion (ICF) facility. N31, one type of neodymium doped phosphate glasses, was developed for high peak power laser facility applications in China. The composition and main properties of N31 glass are given, together with those of LHG-8, LG-770, and KGSS- 0180 Nd:phosphate laser glasses, from Hoya and Schott, and from Russia. The technologies of pot melting, continuous melting, and edge cladding of large size N31 phosphate laser glass are briefly described. The small signal gain profiles of N31 glass slabs from both pot melting and continuous melting at various values of the pumping energy of the xenon lamp are presented. N31 glass is characterized by a stimulated emission cross section of 3:8 � 10??20 cm2 at 1053 nm, an absorption coefficient of 0.10–0.15% cm??1 at laser wavelength, small residual stress around the interface between the cladding glass and the laser glass, optical homogeneity of �2 � 10??6 in a 400 mm aperture, and laser damage threshold larger than 42 J/cm2 for a 3 ns pulse width at 1064 nm wavelength.
neodymium phosphate laser glass large aperture glass ICF facility High Power Laser Science and Engineering
2014, 2(1): 010000e1





